Check out Auron AI and Aurum AI — Deep Learning–driven AI Trading Bots available on the MQL5 Marketplace for free trial demos.
How Deep Learning is Redefining AI Forex Trading
The evolution of global financial markets from human-driven floor trading to fully electronic, sub-millisecond execution environments has fundamentally altered how price discovery occurs. In this setting, predictive advantage is no longer derived from intuition or isolated indicators, but from computational systems capable of extracting structure from noise at scale.
Early AI forex trading systems were largely extensions of classical econometrics. Linear regression, ARIMA, and volatility models such as GARCH were deployed under assumptions of weak stationarity, normality, and equilibrium efficiency as formalized by the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH). While mathematically tractable, these assumptions are routinely violated in live forex markets.
Foreign exchange price dynamics are inherently non-linear, path-dependent, and reflexive. Liquidity fragmentation, asymmetric information, feedback loops, and regime shifts introduce structural complexity that linear models are fundamentally incapable of representing. As a result, their predictive power decays rapidly when exposed to new market conditions.
Deep learning addresses these limitations directly. Rather than imposing structure through hand-crafted features, deep neural networks learn hierarchical representations from data itself. This allows modern machine learning forex systems to operate on raw price sequences, multi-timeframe tensors, limit order book depth, and contextual signals simultaneously.
This article examines the three architectural foundations underlying contemporary AI forex trading algorithms: Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), and Transformer-based attention models. Together, they form the backbone of state-of-the-art ML forex price prediction systems.
1. The Temporal Engine: LSTM Networks in Financial Time Series
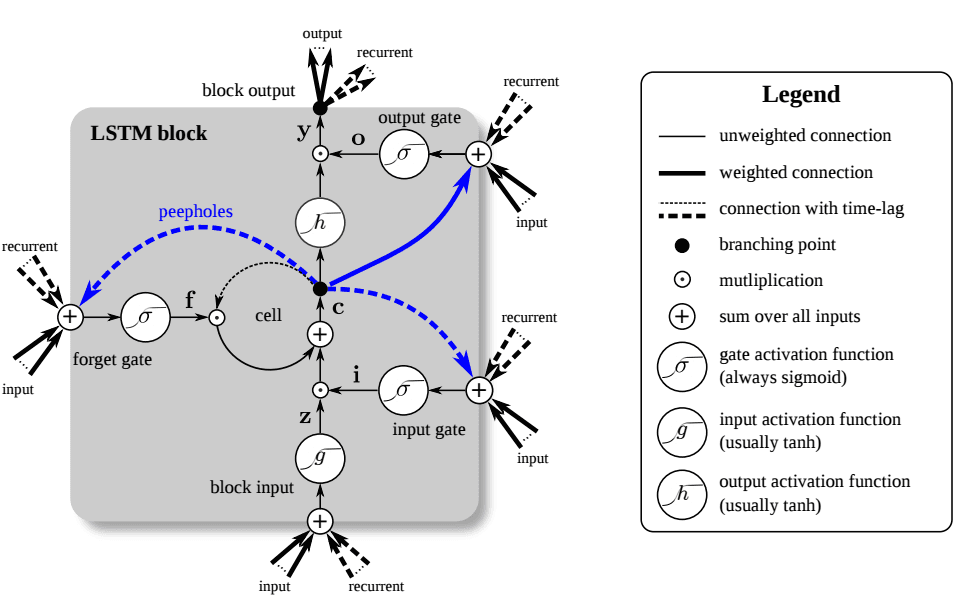
Figure 1: A Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) unit. The LSTM unit has four input weights (from the data to the input and three gates) and four recurrent weights (from the output to the input and the three gates). Peepholes are extra connections between the memory cell and the gates, but they do not increase the performance by much and are often omitted for simplicity. Image by Klaus Greff and colleagues as published in LSTM: A Search Space Odyssey. Image by Klaus Greff and colleagues as published in LSTM: A Search Space Odyssey. Image source: NVIDIA
One of the defining challenges in AI trading bots is learning from temporal dependency. Forex markets exhibit long-memory effects: volatility clustering, delayed reactions to macroeconomic events, and persistent directional bias during regime phases.
Standard recurrent neural networks model temporal structure through a recursive update of the hidden state:
At each timestep , the hidden state is computed as a non-linear transformation of two components: the previous hidden state , which carries accumulated historical information, and the current input , which represents the latest market observation. The weight matrix determines how strongly past information influences the present, while controls the impact of new input, and provides a constant bias term.
Because this same transformation is applied repeatedly across time, gradients during training must propagate through successive multiplications by . As the sequence length increases, these gradients shrink exponentially, causing the contribution of from distant timesteps to approach zero. This vanishing gradient effect makes long-range dependencies effectively invisible to the model, limiting its ability to learn persistent market dynamics.
LSTMs resolve this by introducing an explicit memory cell that evolves additively rather than multiplicatively, allowing information to persist across hundreds or thousands of timesteps.
Gate-Level Dynamics
Each LSTM unit maintains a cell state and a hidden state . Information flow is regulated by three gates:
Forget Gate
This gate controls which components of historical memory are retained. In forex applications, it allows the model to discard outdated volatility spikes or session-specific noise once market conditions normalize.
Input Gate and Candidate Memory
These terms govern how new information—such as momentum shifts, volume expansion, or order-flow imbalance—enters long-term memory.
Cell State Update
The additive update preserves gradient flow, enabling AI forex trading systems to model regime persistence rather than short-lived fluctuations.
Output Gate
The hidden state feeds prediction heads responsible for directional classification, probability estimation, or execution logic in live trading environments.
2. Structural Pattern Recognition with Convolutional Neural Networks
Where LSTMs specialize in temporal dependency, Convolutional Neural Networks specialize in spatial structure. In AI forex trading, CNNs are applied when market data is represented as structured matrices rather than scalar sequences.
Examples include multi-timeframe OHLC grids, stacked technical indicator maps, and limit order book tensors where price levels and depth form orthogonal dimensions.
Convolution as Market Feature Extraction
A convolution operation applies a learnable kernel to an input matrix :
Think of this as sliding a small "detector window" (the kernel ) across your market data (the input ). At each position , the operation multiplies overlapping values and sums them up to produce a single output value .
In trading terms: imagine is a 2D representation of price action—rows could be different timeframes, columns could be sequential candles. The kernel learns to recognize specific patterns (like a doji followed by engulfing candle). As it slides across the data, it outputs high values wherever that pattern appears, regardless of the absolute price level.
This operation detects local structural patterns independent of absolute price. As a result, CNN-based AI trading algorithms can identify liquidity compression, imbalance zones, and microstructure asymmetries that are invisible in raw time series.
Stacked convolutional layers progressively abstract these patterns into higher-order representations, while pooling layers introduce robustness to noise and execution artifacts.
In practice, CNNs often act as front-end encoders, feeding spatial representations into LSTM or Transformer modules for temporal and contextual reasoning.
3. Attention-Based Modeling with Transformers
Transformers represent a departure from recurrence altogether. Instead of processing sequences step by step, they evaluate all timesteps simultaneously using self-attention.
This architecture allows ML forex price prediction systems to associate distant events—such as macroeconomic releases or cross-session correlations—with current market behavior without information decay.
Scaled Dot-Product Attention
The "Attention" mechanism is the engine that allows Transformers to move beyond the linear, step-by-step memory of older models. Instead of just remembering the recent past, the model can "look" at the entire historical record and decide which specific moments are relevant to the current market state.
The Equation Breakdown
The mechanism is governed by the following fundamental equation:
To understand how this functions in ML forex price prediction, we can break it down into its four constituent parts:
The Query (), Key (), and Value (): These are learned linear projections of your input data.
- •
The Query (): Think of this as the "search term." It represents the current market state the bot is trying to understand.
- •
The Key (): Think of this as the "index" or "labels" for all historical data points. It represents what each past moment "is about".
- •
The Value (): This is the actual information (price action, volume, sentiment) contained in those past moments.
- •
The Dot Product (): This operation measures the similarity between your current Query and every historical Key. The higher the score, the more relevant that specific historical moment is to your current situation.
The Scaling Factor (): In high-dimensional spaces, dot products can grow very large, which can push the "softmax" function into regions where gradients are extremely small (the vanishing gradient problem). Dividing by the square root of the dimension of the keys () stabilizes the numbers and ensures the model can keep learning efficiently.
The Softmax Function: This converts the raw similarity scores into probabilities that sum to 110. It effectively tells the model: "Give 70% of your attention to the data from three months ago, 20% to yesterday, and ignore the rest"
Conclusion: The Future of AI Forex Trading Systems
Modern AI forex trading systems no longer rely on single-model architectures. Robust performance emerges from hybrid designs that integrate complementary inductive biases:
- •
LSTMs for temporal memory and regime awareness
- •
CNNs for spatial and microstructure feature extraction
- •
Transformers for global context and long-range dependency modeling
As markets continue to evolve, alpha will increasingly favor systems that can see structure, retain memory, and dynamically reweight information. Deep learning provides the mathematical machinery to do all three simultaneously.
In this paradigm, the edge lies not in isolated indicators, but in coherent representations of market reality across time, space, and context.
Find out more about other Machine learning architectures used in forex trading
Happy Trading!